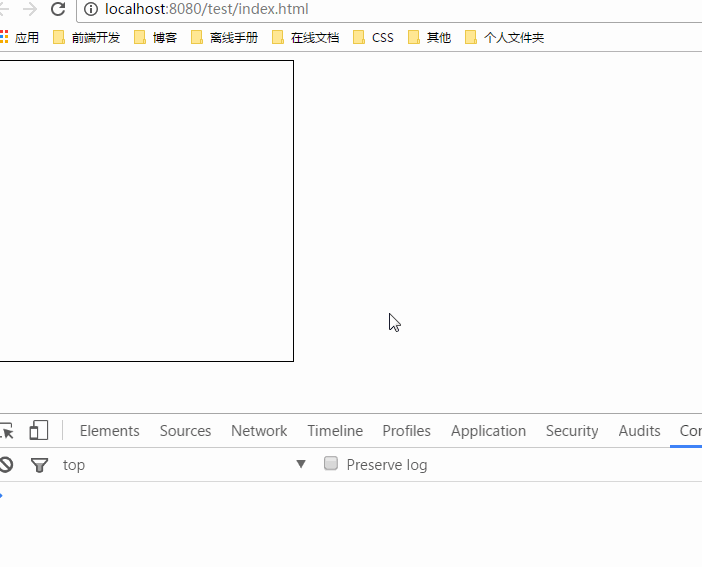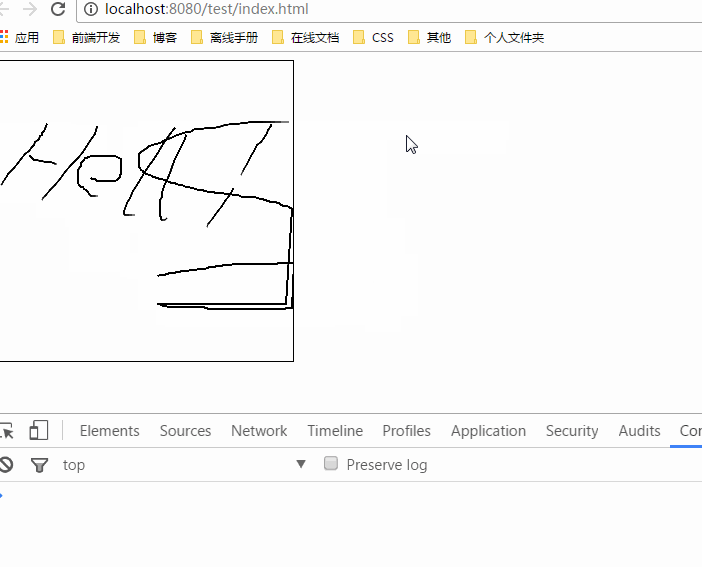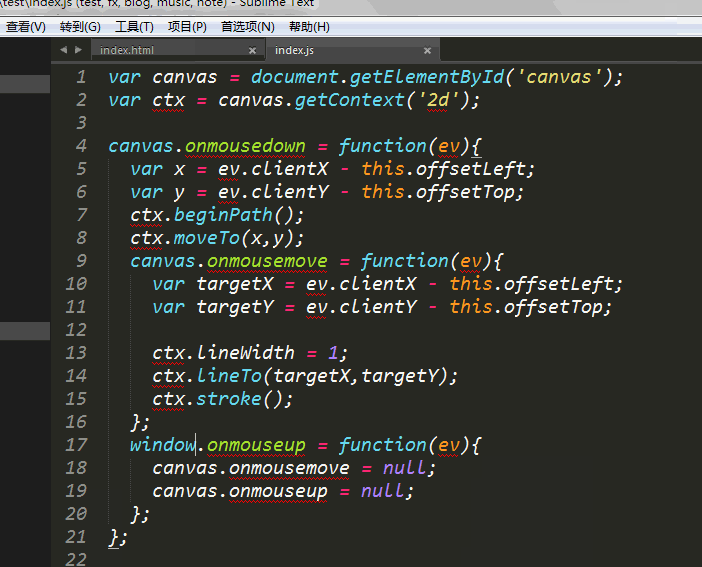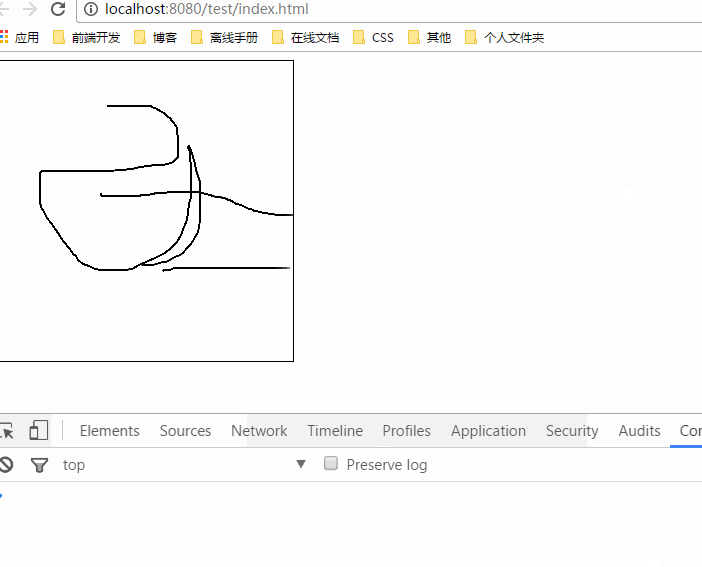
实现思路:监听鼠标按下、移动、松开事件,将鼠标按下的值赋值给moveTo的x和y值,作为起始位置。在移动事件中,将鼠标距离可视区x和y值赋给lineTo,再将路径闭合。以下是具体的代码
Document
以上的原理就是每次按下鼠标都重新开始一条路径,并将画笔移动到鼠标按下的那个位置,当鼠标移动的时候将线画到鼠标所在的位置,然后闭合,一直重复这一过程,最终就会变成我们所要画的形状,当鼠标松开,清空移动事件和松开事件,直到鼠标再次按下开始新的一轮画图。
注意鼠标松开事件要给window或者document加,不然就会出现下面这个情况
给canvas加鼠标松开事件之所以会出现这种情况,是因为我并不是在canvas中松开鼠标的,因此自然就不会执行canvas中的onmouseup事件了,因而当我们再回到canvas中时它依然还会执行onmousemove事件,而如果给window加,就不会有这种问题,因为整个窗口都属于window范围的,只要你在窗口中松开鼠标就会响应onmouseup事件。
2017.02.24更新
完善canvas功能,新增后退,前进,清除功能

清除功能通过canvas上下文对象的clearRect方法实现。
后退和前进功能,我的想法是每画一次就将整个画布的数据push到一个数组中,按前进和后退时再将对应的数据取出来,这个可以通过getImageData和putImageData方法实现,这两个方法的使用可以到http://www.w3school.com.cn/tags/html_ref_canvas.asp中查看,以下是功能的全部代码
function Graffiti(dom,context){ this.canvas = document.querySelector(dom); this.context = this.canvas.getContext("2d"); this.imgList = []; this.prevIndex = 0; this.nextIndex = 0; this.currentIndex = 0; this.init();}Graffiti.prototype = { constructor:this, init:function(){ var _this = this; this.move(function(){ _this.pushImg(); _this.upIndex(_this.imgList.length - 1); }); }, move:function(endCallback){ var _this = this; var canvas = this.canvas; var context = this.context; canvas.onmousedown = function(ev){ var x = ev.clientX - this.offsetLeft; var y = ev.clientY - this.offsetTop; context.beginPath(); context.moveTo(x,y); canvas.onmousemove = function(ev){ var targetX = ev.clientX - this.offsetLeft; var targetY = ev.clientY - this.offsetTop; context.lineWidth = 1; context.lineTo(targetX,targetY); context.stroke(); }; window.onmouseup = function(ev){ canvas.onmousemove = null; canvas.onmouseup = null; endCallback&&ev.target.matches("#canvas")&&endCallback(); }; }; }, back:function(){ this.clear(); this.context.putImageData(this.imgList[this.prevIndex],0,0); this.upIndex(this.prevIndex); }, go:function(){ this.clear(); this.context.putImageData(this.imgList[this.nextIndex],0,0); this.upIndex(this.nextIndex); }, pushImg:function(){ this.imgList.push(this.context.getImageData(0,0,this.canvas.width,this.canvas.height)); }, clear:function(){ this.context.clearRect(0,0,this.canvas.width,this.canvas.height); }, upIndex:function(index){ if(index===0){ this.prevIndex = 0; }else{ this.prevIndex = index - 1; } if(index===this.imgList.length-1){ this.nextIndex = index; }else{ this.nextIndex = index + 1; } this.currentIndex = index; }};var can = new Graffiti("#canvas");var back = document.getElementById("back");var go = document.getElementById("go");var clear = document.getElementById("clear");back.onclick = can.back.bind(can);go.onclick = can.go.bind(can);clear.onclick = can.clear.bind(can); 注意在window.onmouseup的时候有个坑,因为我是在这里面执行储存信息的,因此会出现一个问题,就算我不是在canvas上提起也会相应这个事件,所以在里面我加了一个判断,如果不是canvas就不储存
ev.target.matches("#canvas") 总的来说,这几个功能的难点就在于,你要知道有哪些API,以及如何取储存数据和取数据。